지네릭스(Generics)
지네릭스(Generics)란?
- 컴파일시 타입을 체크해 주는 기능(compile-time type check)
- 객체의 타입 안정성을 높이고 형변환의 번거로움을 줄여줌

- 예시
아래와 같은경우 컴파일러가 찾아내지못한다. ArrayList는 Object의 배열이므로, list.get(2)가 Object 객체를 반환하므로 이를 형변환 가능할것이라고 생각된다.
하지만 실제 runtime exception이 발생한다. 이유는 실제로는 String 객체를 Integer 로 형변환이 불가능하기때문이다
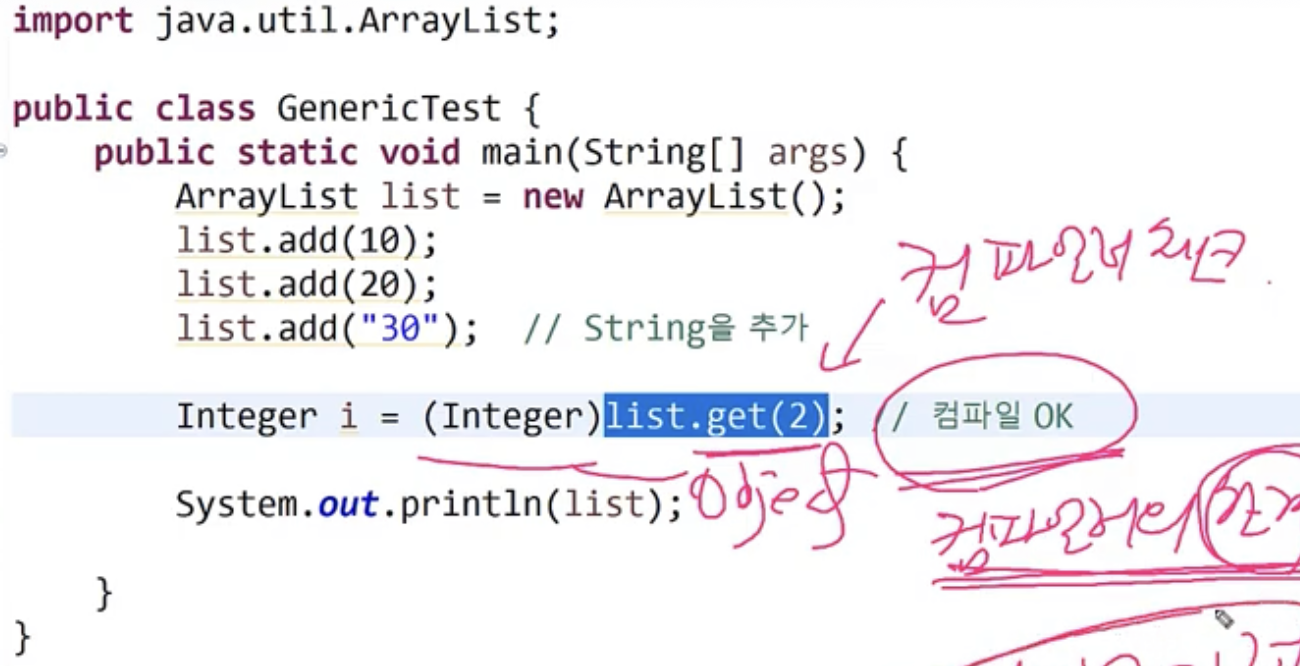
- 이를
ArrayList<Integer> = new ArrayList<Integer>();로 제네릭을 사용한다면, 컴파일러가 오류를 찾아낼수있다.

타입 변수
- 지네릭 클래스를 작성할 떄, Object타입 대신 타입 변수(E)를 선언해서 사용
- 원래는 일반클래스는 모두 Object타입을기반으로 생략되어있다.

타입변수에 대입하기
- 객체를 생성시, 타입 변수(E)대신 실제 타입(Tv)을 지정(대입)
- 참조변수, 생성자의 타입변수등 모두 실제 타입으로 변경해줘야함.
- 형변환 생략 가능하도록 메서드포함 모두 실제타입으로 변경되어 객체생성됨

지네릭스 용어
- Box
지네릭 클래스, 클래스명 <타입변수> 형태 타입 변수 또는 타입 매개변수 (T는 타입 문자) - Box
일반 클래스, 원시 타입(raw type)

지네릭 타입과 다형성
- 참조 변수와 생성자의 대입된 타입은 일치해야한다.(무조건항상 타입은 일치해야한다
혹시 다르게하고싶다면 와일드카드해야함) - 지네릭 클래스간의 다형성은 성립
(대입된 타입은 무조건 일치해야함) - 매개변수의 다형성도 성립
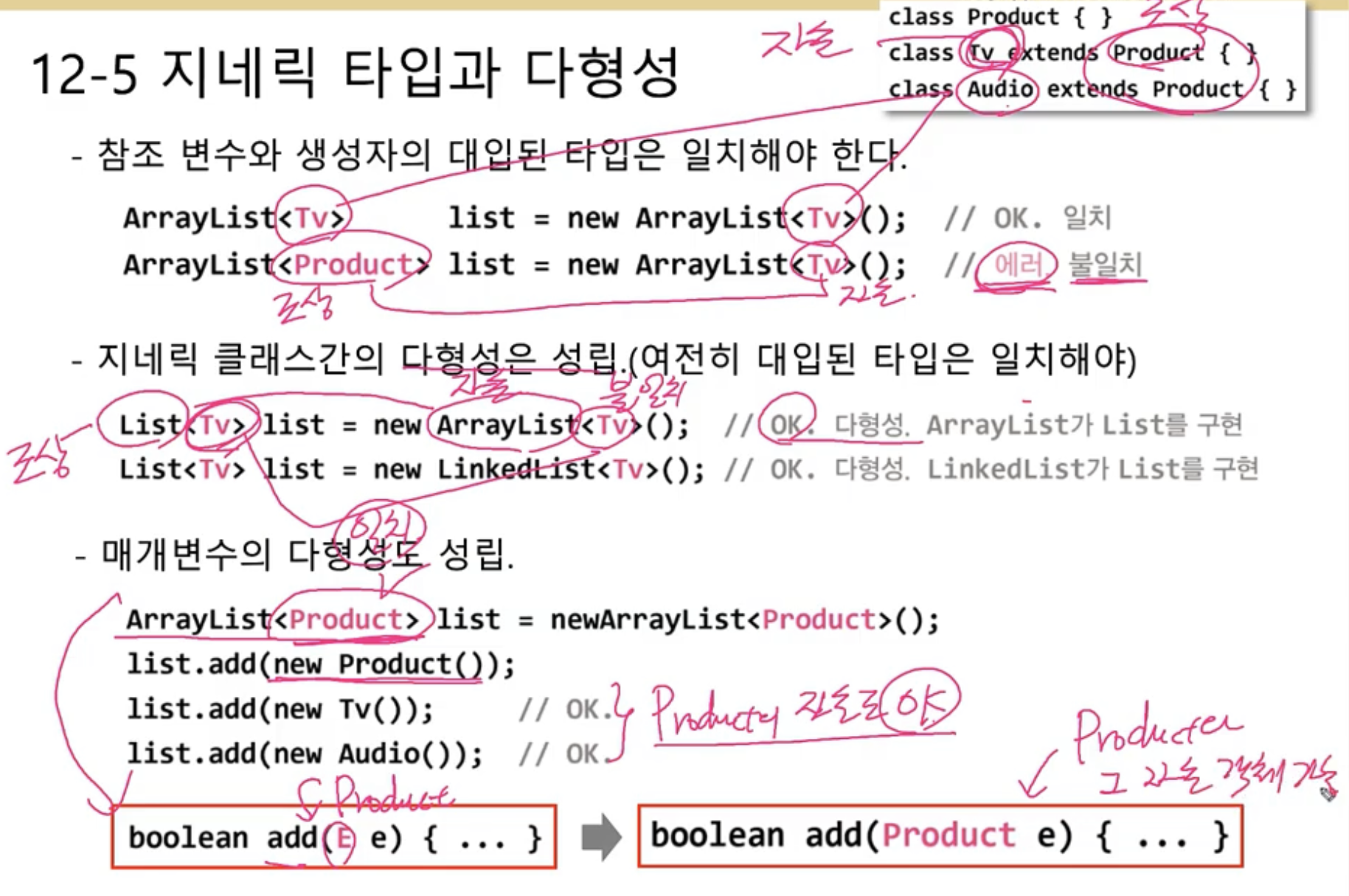
- Object대신 타입변수덕분에 Product 타입이 들어갔고, 이는 get함수또한 Product타입으로 반환한다. 따라서 만약 Tv타입이 필요하다면 Tv tv = (Tv) g.get() 형변환 필수
- List
tvList = new ArrayList ; 는 가능 타입일치, 다형성
1 | import java.util.*; |
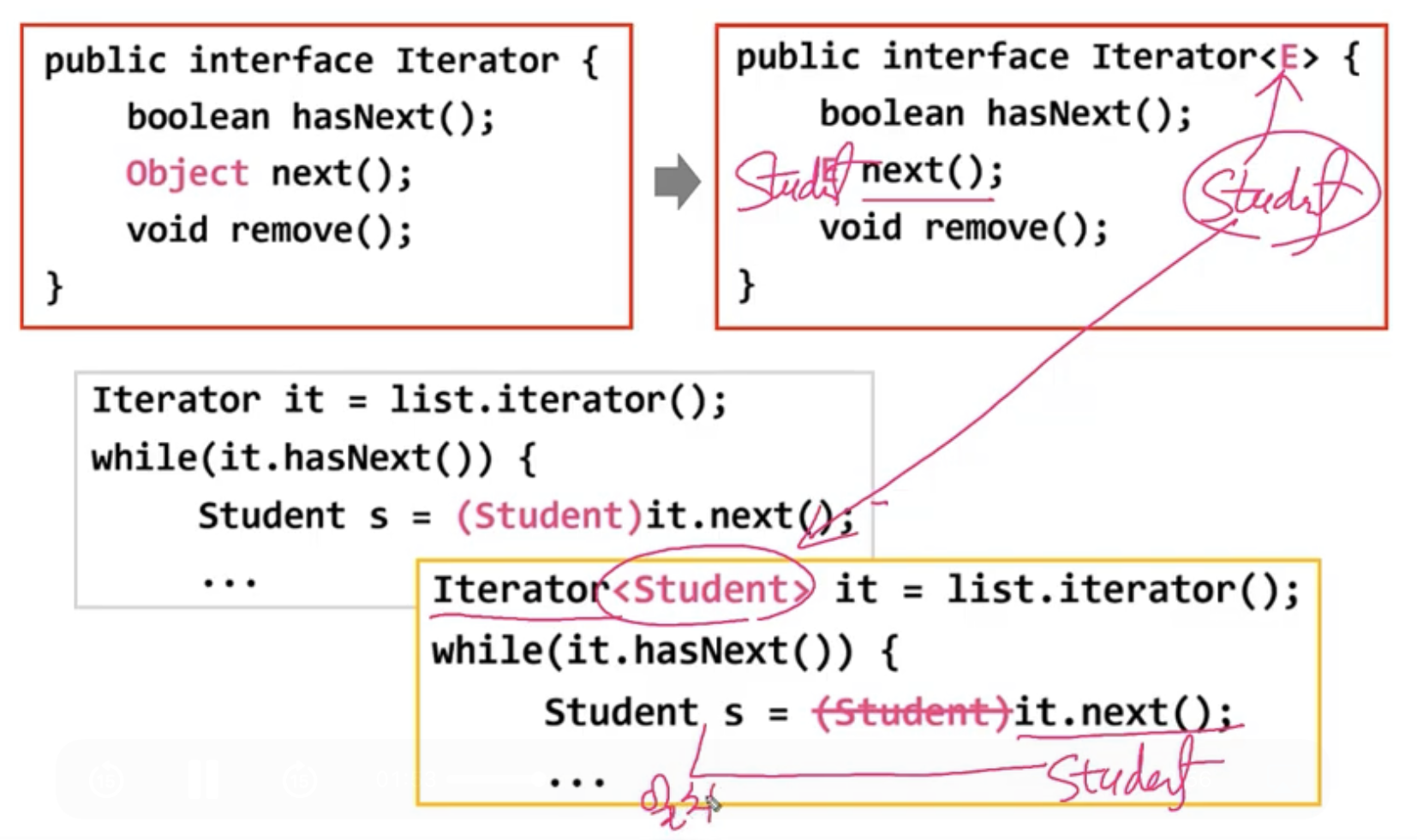
Iterator
- 클래스를 작성할 때, Oject타입 대신 T와 같은 타입 변수를 사용
- 제네릭 이터레이터 사용시 형변환 필요없어진다
(기존것은 Object반환하므로 형변환필요했음)
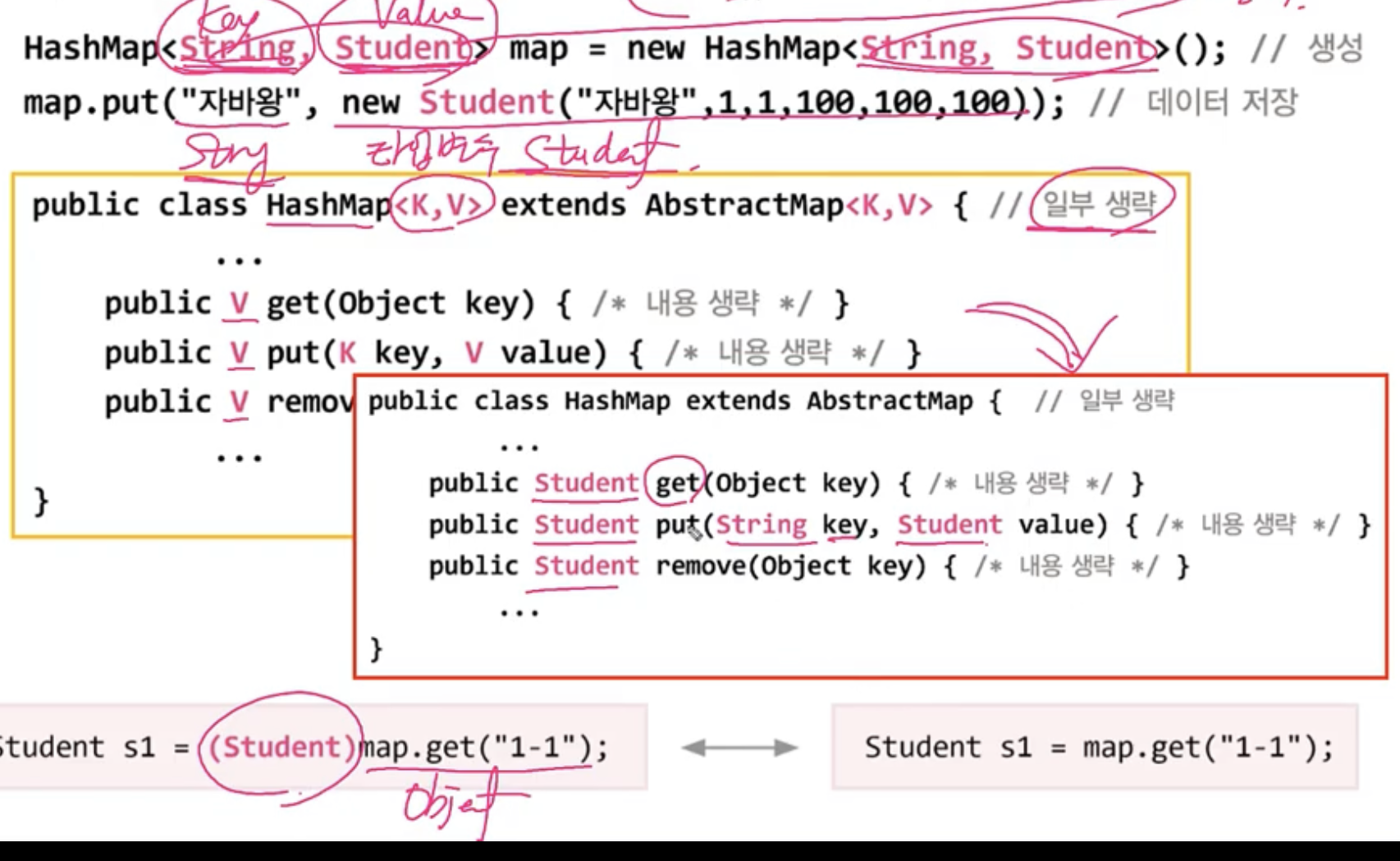
HashMap <K,V>
- 여러 개의 타입 변수가 필요한 경우, 콤마(,)를 구분자로 선언
- 예시도 마찬가지로 형변환 불필요
제한된 지네릭 클래스
- extends로 대입할 수있는 타입을 제한(클래스, 인터페이스사용법동일)
- 아래 예시는 T에 대입할수있는 타입은 Fruit의 자손만가능

1 | import java.util.ArrayList; |
지네릭스의 제약
타입 변수에 대입은 인스턴스 별로 다르게 가능
- static멤버에 타입 변수 사용 불가
(static은 모든 인스턴스 공통이므로) - 배열 생성할때 타입 변수 사용불가. 타입 변수로 배열 선언은 가능
(new T) 불가능

와일드 카드 <?>
- 하나의 참조 변수로 대입된 타입이 다른 객체를 참조 가능

- 메서드의 매개변수에 와일드 카드 사용
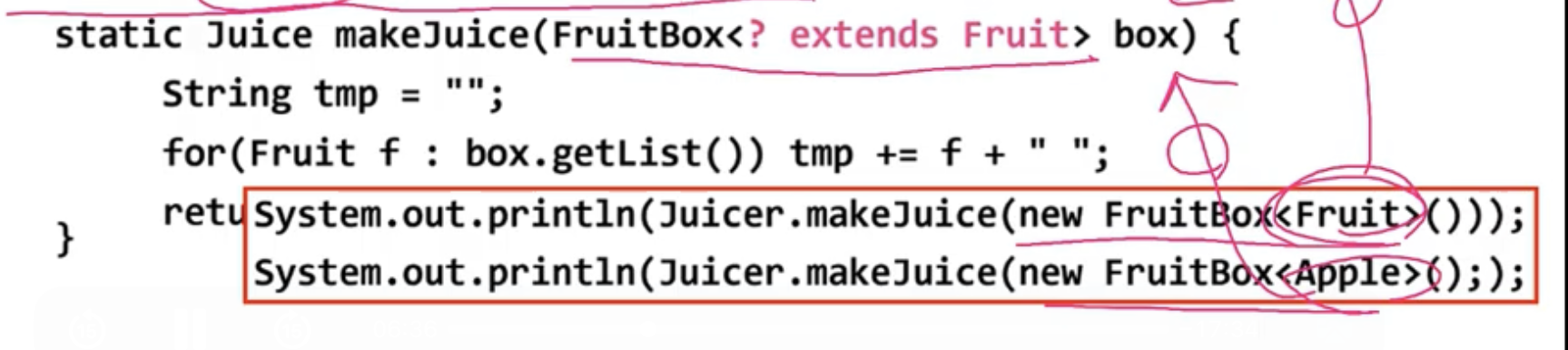
지네릭 메서드
- 지네릭 타입이 선언된 메서드(타입 변수는 메서드 내에서만 유효)
- 클래스의 타입 매개변수
와 메서드의 타입 매개변수 는 별개

- 메서드를 호출할 때마다 타입을 대입해야 (대부분 생략 가능)

지네릭 타입의 형변환
- 지네릭 타입과 원시 타입 간의 형변환은 바람직 하지 않다.(경고 발생)
- 권장하지않음!! 원시타입과 꼭 구별하여 사용하기
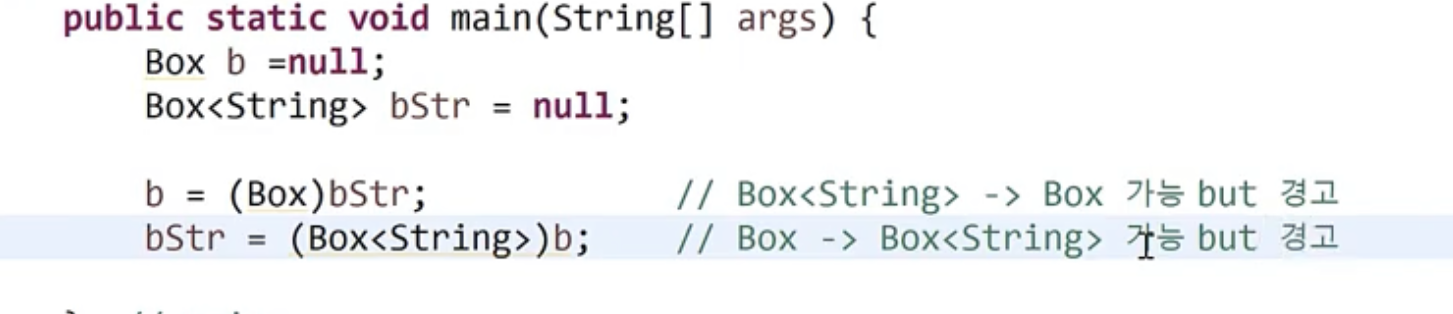
- 와일드 카드가 사용된 지네릭 타입으로는 형변환 가능

지네릭 타입의 제거
- 컴파일러는 지네릭 타입을 제거하고, 필요한 곳에 형변환을 넣는다( 결국 지네릭 타입은 없어진다!!!)

열거형(enum) (???)
- 관련된 상수들을 같이 묶어놓은것, Java는 타입에 안전한 열거형을 제공
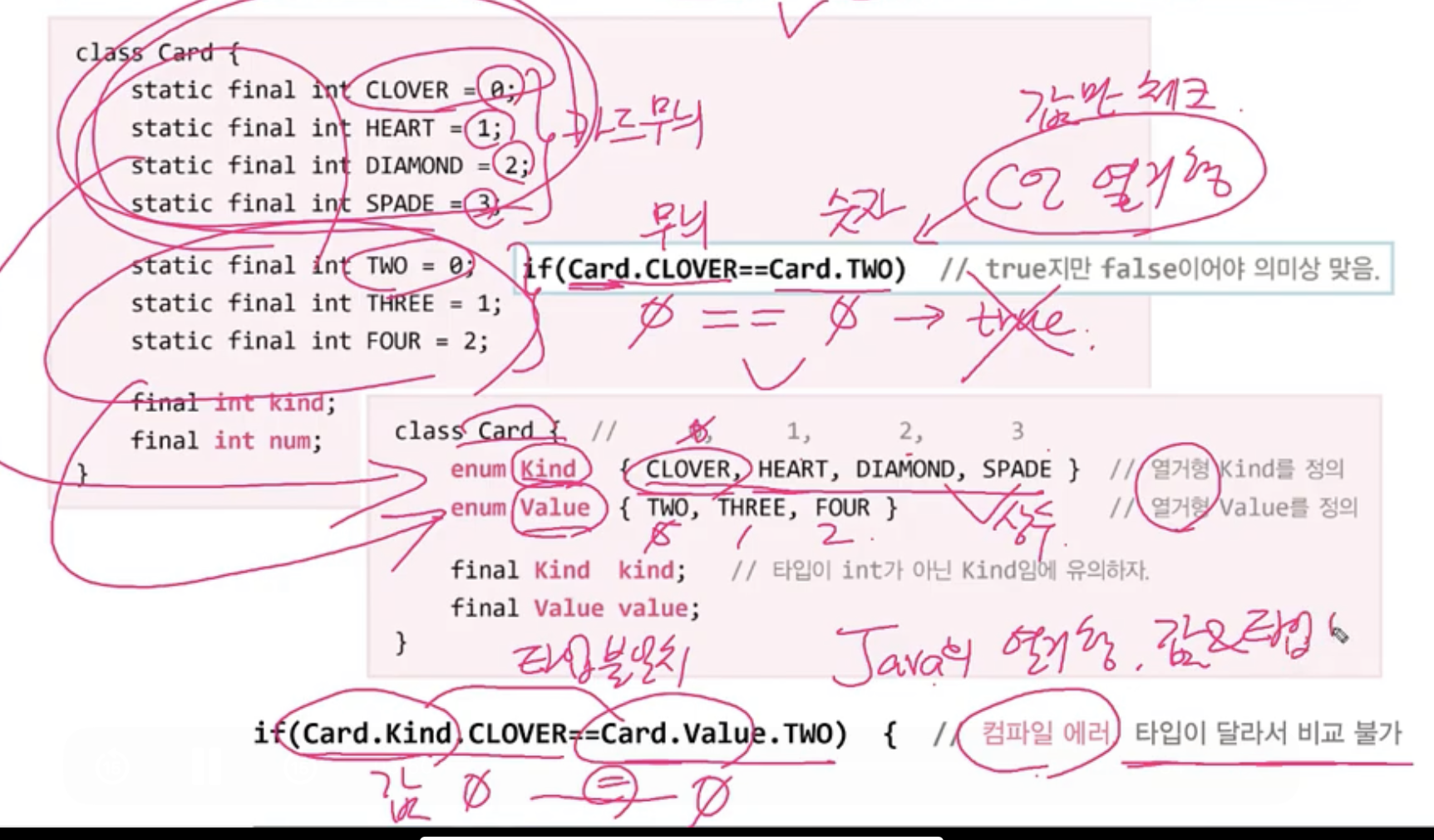
열거형의 정의와 사용
- 열거형을 정의하는 방법

- 열거형 타입의 변수를 선언하고 사용하는 방법
- 열거형 상수의 비교에 ==와 compareTo() 사용가능

열거형의 조상 - java.lang.Enum
- 모든 열거형은 Enum의 자손이며, 아래 메서드를 상속받는다.
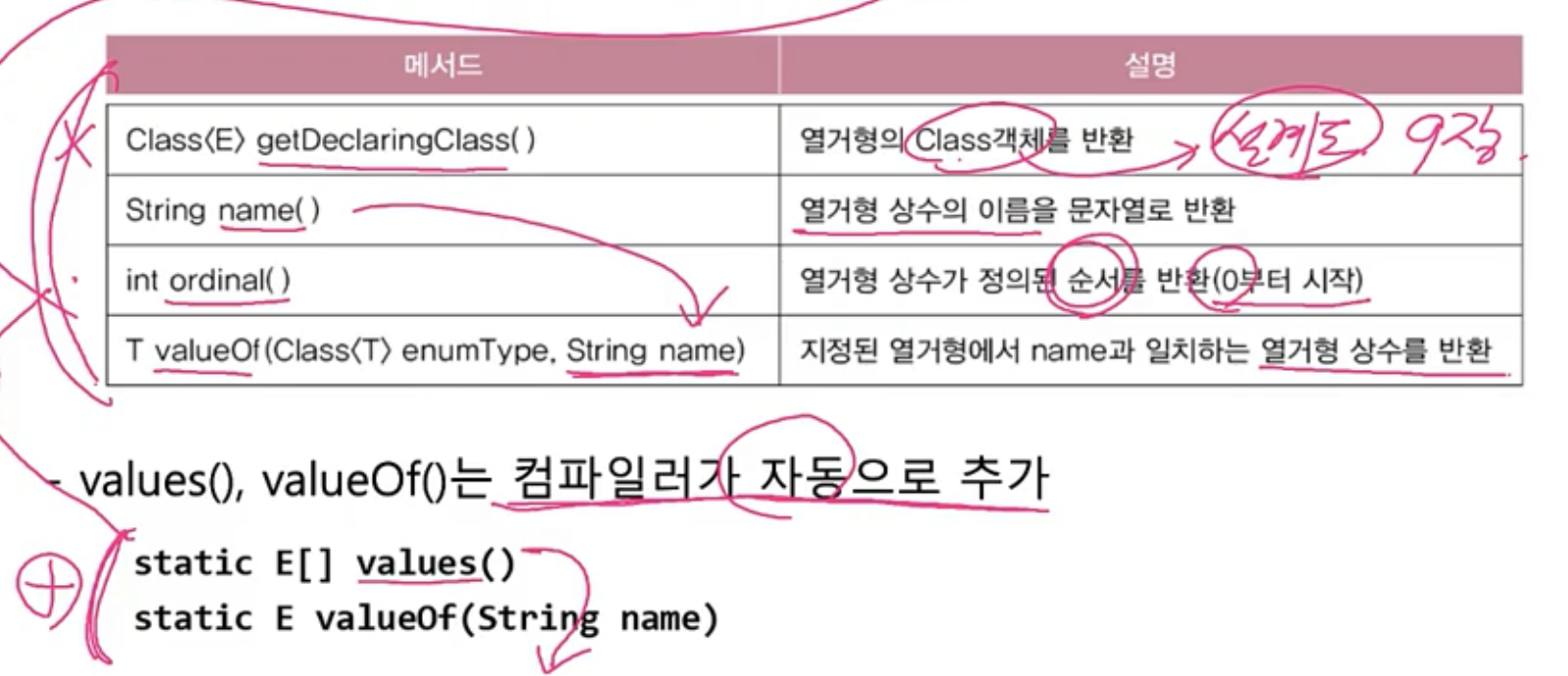
- 예시
1 | enum Direction { EAST, SOUTH, WEST, NORTH } |
열거형에 멤버 추가하기
- 불연속적인 열거형 상수의 경우, 원하는 값을 괄호()안에 적는다
- 괄호()를 사용하려면, 인스턴스 변수와 생성자를 새로 추가해 줘야한다.
- 열거형의 생성자는 묵시적으로 private이므로, 외부에서 객체생성 불가
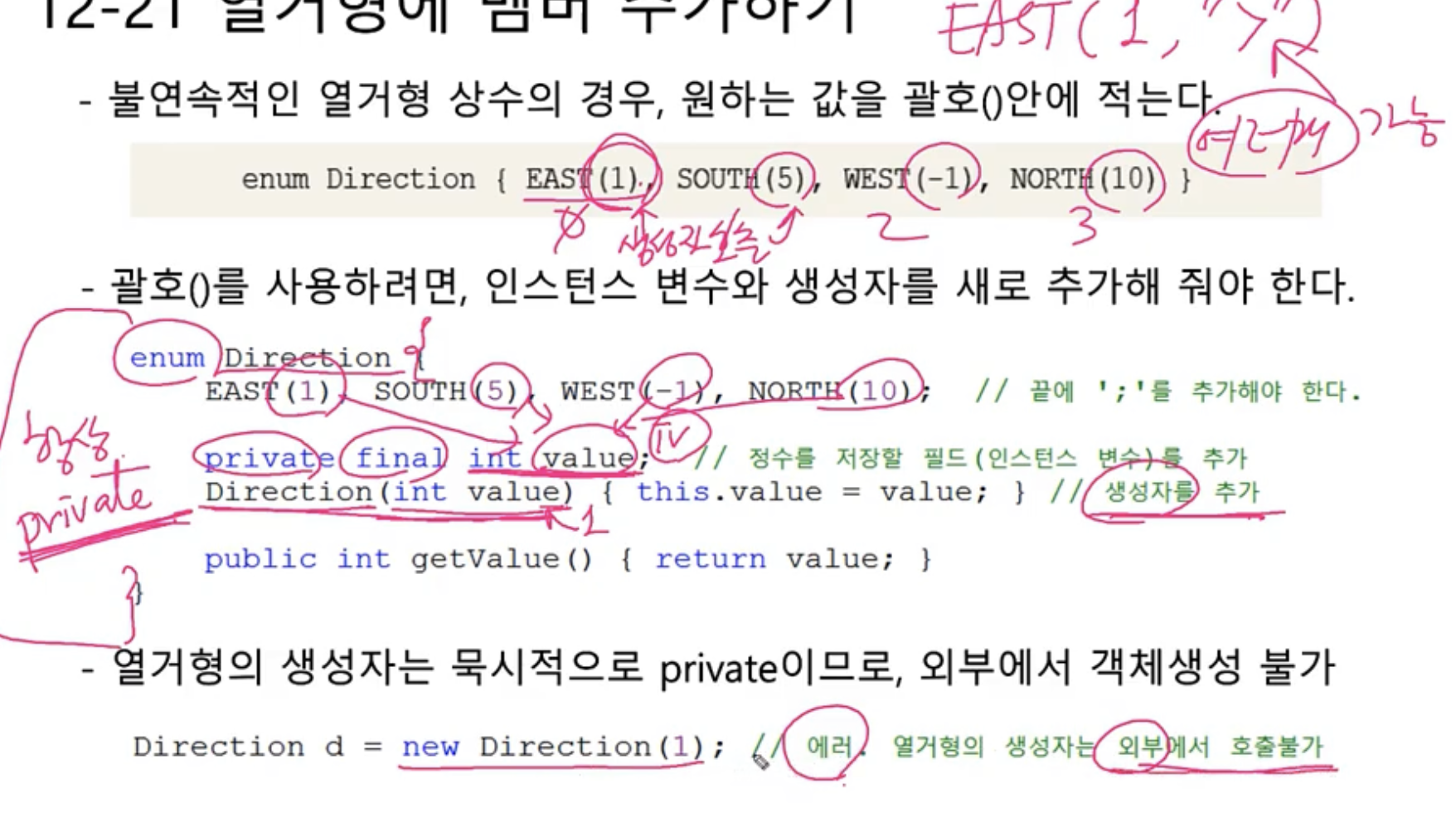
1 | enum Direction2 { |
애너테이션이란?
- 주석처럼 프로그래밍 언어에 영향을 미치지 않으며, 유용한 정보를 제공
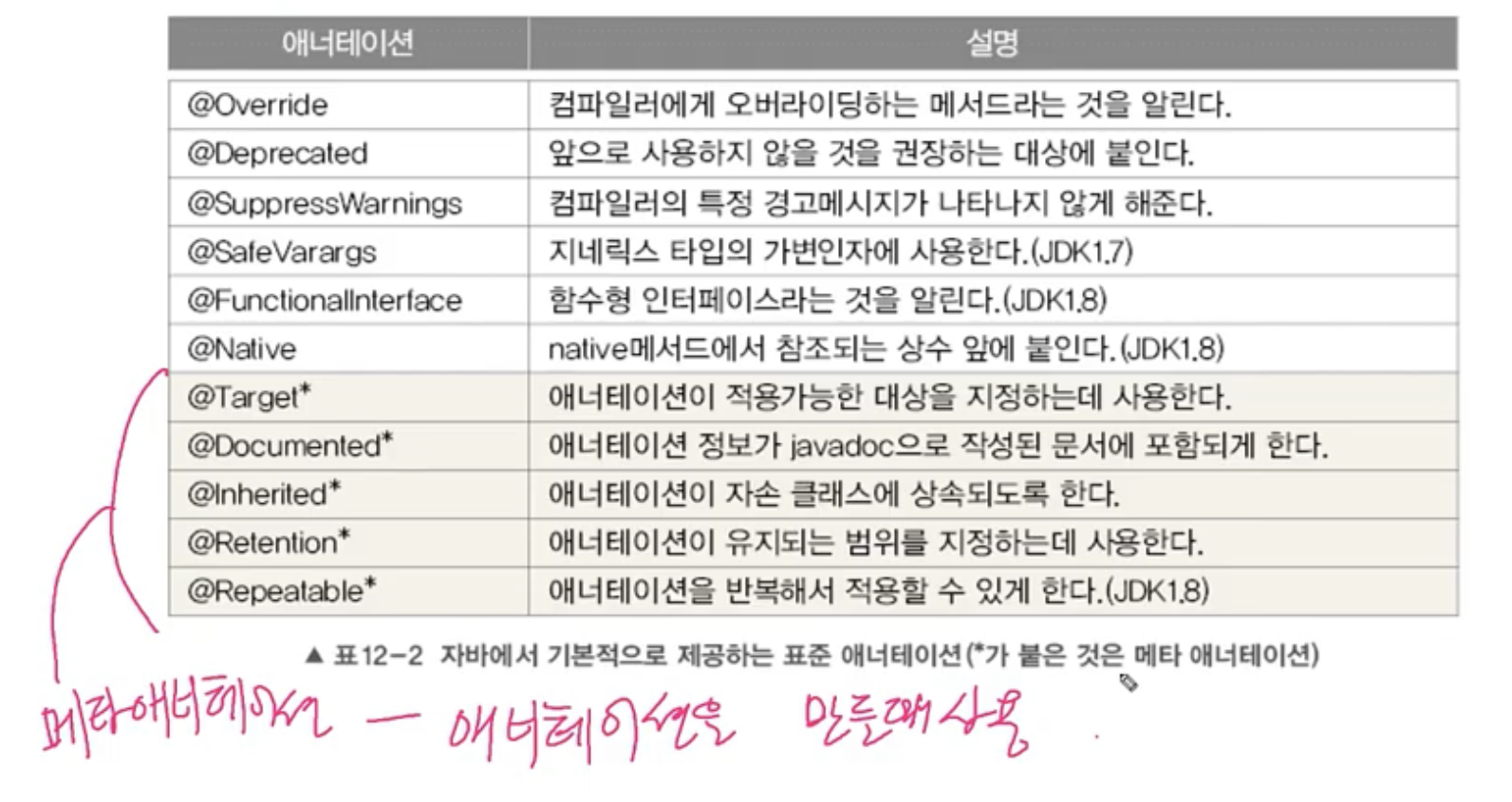
표준 애너테이션
- Java에서 제공하는 애너테이션
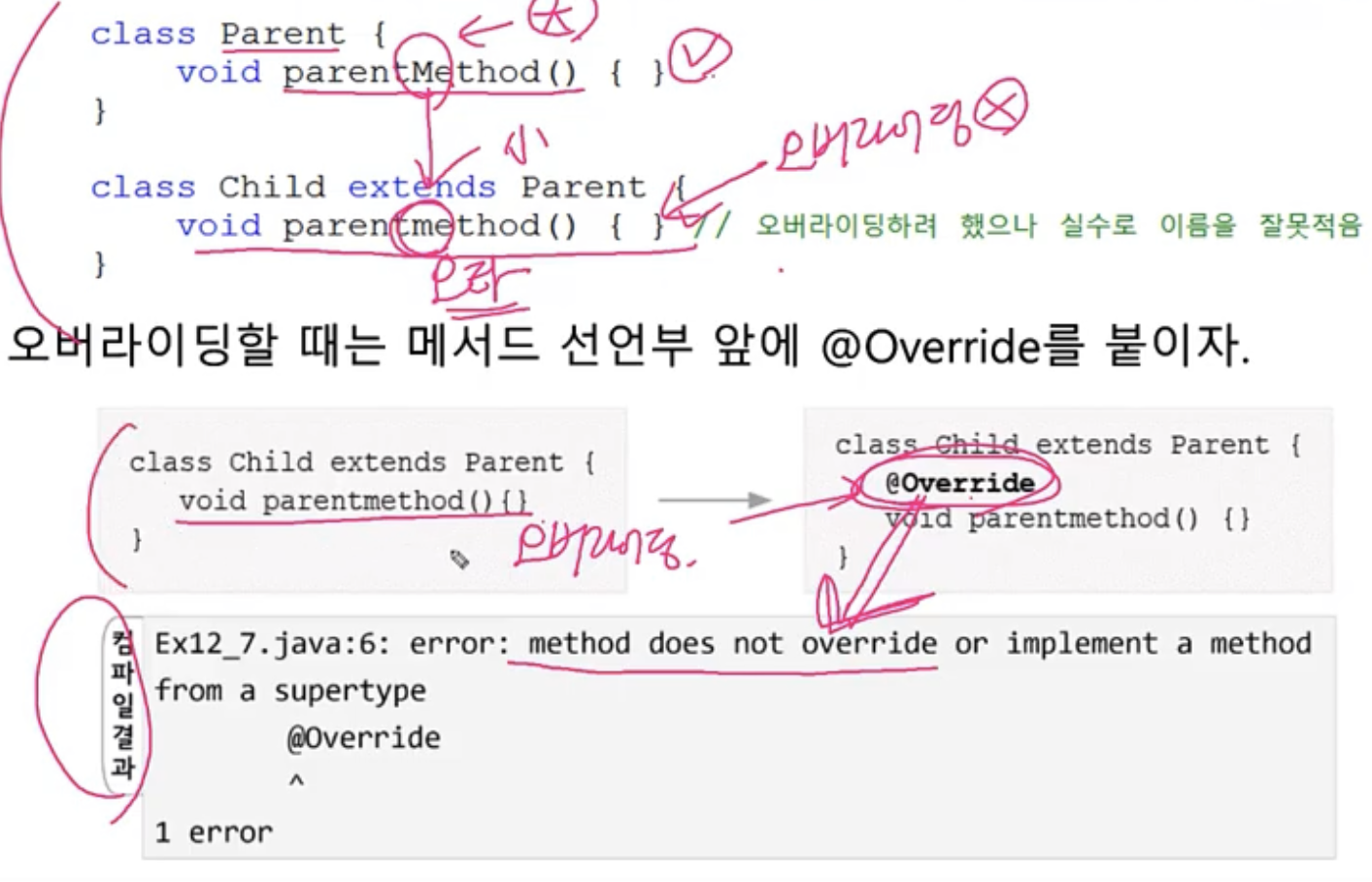
@Override
- 오버라이딩을 올바르게 했는지 컴파일러가 체크하게 한다
- 오버라이딩할 때 메서드이름을 잘못적는 실수를 하는 경우가 많다
- 항상 오버라이딩시에 선언부 위에 @Override 붙여주기
(실수막아줌)
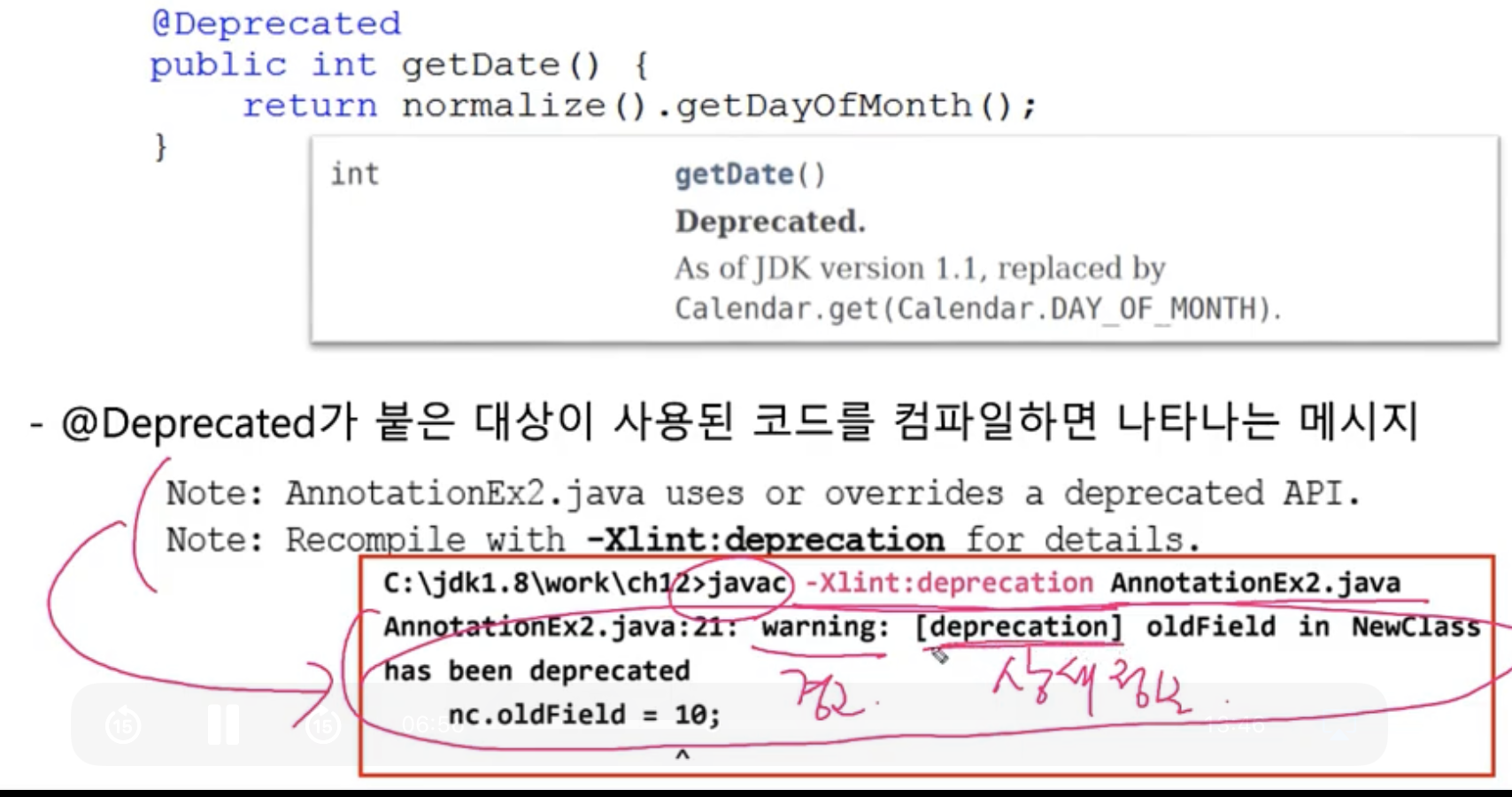
@Deprecated
- 앞으로 사용하지 않을 것을 권장하는 필드나 메서드에 붙인다.
- @Deprecated의 사용예, Date클래스의 getDate()
@FunctionalInterface
- 함수형 인터페이스에 붙이면, 컴파일러가 올바르게 작성했는지 체크
- 함수형 인터페이스에는 하나의 추상메서드만 가져야 한다는 제약이있음
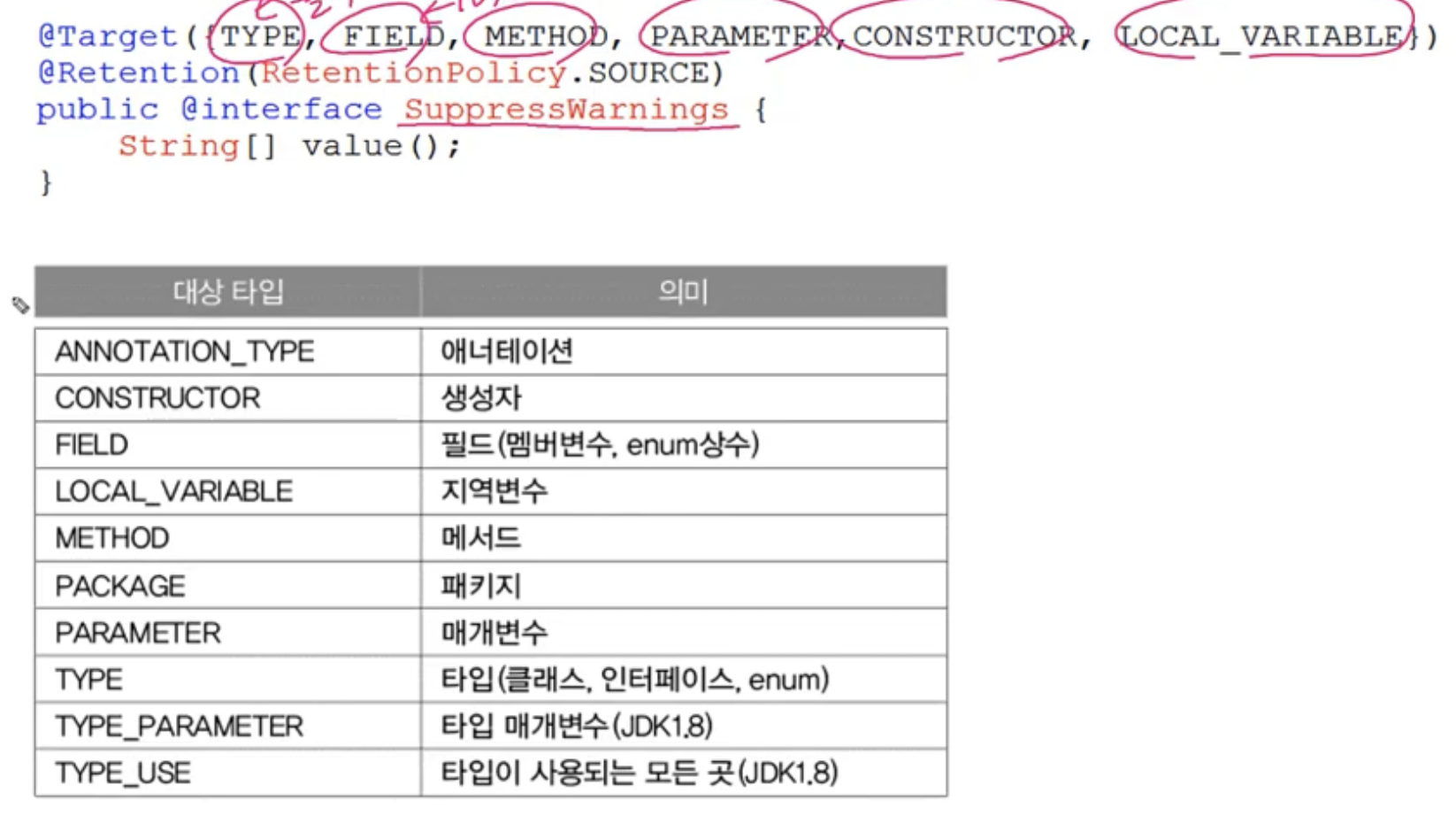
@SuppressWarnings
- 컴파일러의 경고메시지가 나타나지 않게 억제한다.
- 괄호 () 안에 억제하고자하는 경고의 종류를 문자열로 지정
- 지정한 경고는 나오지 않음
메타 애너테이션
- 애너테이션을 위한 애너테이션
- java.lang.annotation패키지 포함됨
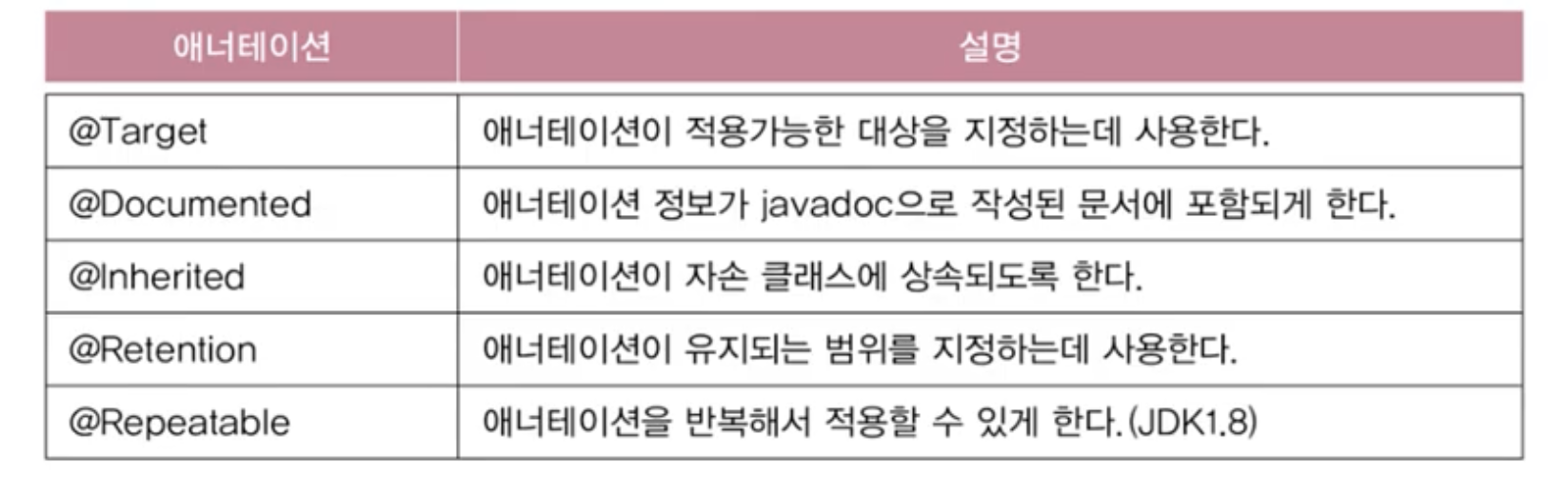
@Target
- 애너테이션을 정의할 때, 적용대상 지정에 사용
@Retention
- 애너테이션이 유지되는 기간을 지정하는데 사용
